Labels
Scientific Processes in Biology
Scientific Processes in Biology
Biology, just like other science subjects, involves carrying out experiments. When studying living things simple observation can be made by using our own senses i.e. sight, smell, touch, taste and hearing. The senses can be detected by our sense organs i.e. eye for sight, nose for smell, skin for touch, tongue for taste and ear for hearing.
To Use Own Sense Organs to Make Correct Observations
Use own sense organs to make correct observations
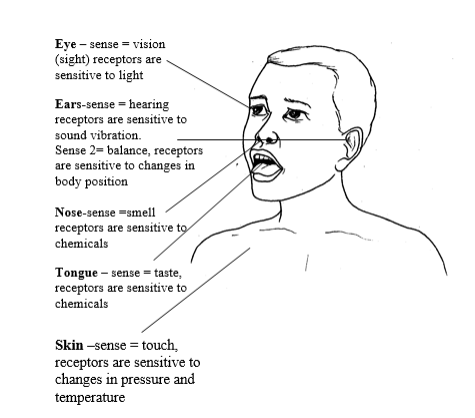
The body sense organs
Measurements of Mass, Length, Temperature and Pulse Rate
Take measurements of mass, length, temperature and pulse rate
Measurements: When carrying out biological investigation measurements like mass, time, temperature, and length are unavoidable.
Instruments used for various measurements:
- Beam balance – for measuring mass
- Thermometer – for measuring temperature
- Clock/stopwatch – for measuring time
- Ruler – for measuring length
- Pulse rate can be measured by using a stethoscope or by pressing the fingers firmly on the skin.
The study of biology like any the science subject involves scientific processes. The scientific processes involved in the study of biology include observation, measurement and experimentation. Through these processes the study of biology becomes possible.
OBSERVATION
Through observation we can learn many scientific phenomena. Observation is made by using our own sense organs. There are five sense organs in the human body which are eyes, ears, the nose, the tongue, and the skin. Each of these organs is specific to a certain type of observation.
The following are sense organs and their associated functions in observation.
Eyes
How can you differentiate between the colors of an egg from that of a ripe pawpaw? In this case in order to answer this question correctly, you must be able to make correct observation. By using your eyes you can observe differences in colors of the two things given and then tell their differences.
We use our eyes as a sense organ for vision. By using our eyes we are able to see and differentiate sizes, colours and shapes of various organisms and hence we can learn about them.
Ears
How can you distinguish between the sound produced by a singing bird and a roaring lion? Sometimes you can just use your ears to study various biological concepts. For example many organisms produce different sounds which we can use to identify them.
Therefore, it is easy for a biologist to know an organism just by hearing the sound without even seeing it. This proves how your ears are very important organs in scientific studies because they are used to identify and differentiate sounds of various living organisms.
Nose
Sometimes in the scientific study we need to smell in order to identify and distinguish between various things. For example, how can you distinguish the smell of a ripe banana from that of a ripe pineapple? As a scientist you must be able to use your nose as a sense organ effectively and successfully. BUT avoid smelling anything in the laboratory without the permission from your teacher or laboratory technician.
Tongue
We use tongue to taste various things. By use of tongue we can differentiate various tastes and be able to discover the type of the taste concerned. For example, one can differentiate salt from sugar solutions by just tasting using the tongue. BUT avoid tasting anything in the laboratory unless you are told do so by the teacher or laboratory technician.
Skin
We can use the skin as a sense organ to detect heat, temperature, pressure and even pain. For example, during a hot day you feel hot while during cold days you feel cold. Even if you close your eyes, and someone rubs your skin using a block of ice, you can simply tell it by just feeling the coldness it imparts to the surface of your skin.
This group of students are conducting an experiment on ‘food tests’ in the school laboratory. Can you tell the sense organs they are using in their study?

MEASUREMENT
Though we can use our sense organs to make observations, the observations alone are not so reliable. Every sense organ has its weakness. Since science lies upon measurable quantities there is a need of measurement. Scientists have been able to design ways to take measurements of various things. Some of the quantities which can successfully be measured include mass, temperature, length and pulse rate.
Measurement of length
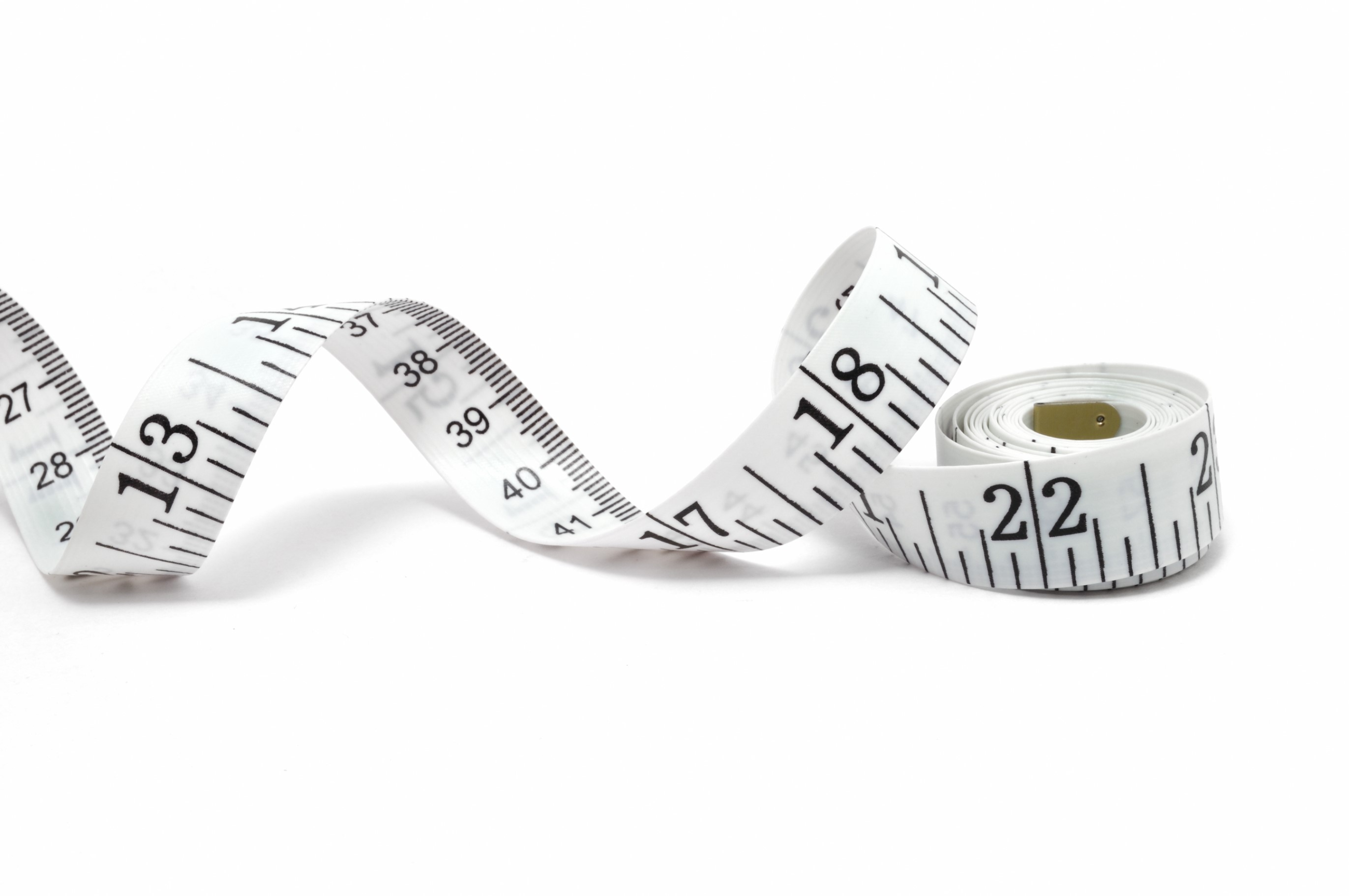
We can use eyes to observe the length of various objects. However, our eyes can just tell which object is longer than the other but can not tell us what the exact length of each object is. Tape measure is one of the common instruments that are used for measuring length in our every day life.
Tape measure, an instrument for measuring length

Measurement of mass
A scientist or biologist must have a standard way of measuring mass of a substance. Sense organs cannot give us the true value of mass of a substance. This can be done by using beam balance which is a special instrument for measuring mass of a substance.
Beam balance

Measurement of temperature
We can take the measurement of temperature of a substance just by using our sense organs. For example, by touching something you can tell whether a particular thing is hot or cold. However, you cannot tell exact temperature of an object.
Therefore, to be able to know the exact temperature you need to use an instrument specially designed for measuring the temperature. This is instrument is the thermometer. Using thermometers we are able to know the exact temperature of an object.
Thermometer

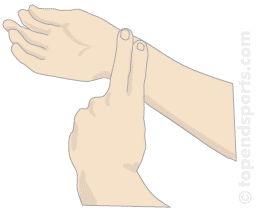
Measurement of pulse rate
Pulse rate refers to average beating of your heart. You can find how fast your heart is beating, that is your heart rate, by feeling your pulse.
How to measure your pulse rate
- Sit down comfortably on a chair with the palm of your hand facing upwards.
- Gently place the index and middle fingers of your other hand on your wrist (see the diagram below). Can you feel your pulse as a repeated throb?
- If necessary change the position of your finger until you can feel your pulse rate well. Count the number of heart beats in one minute.
- Repeat step 3 four times.
- Write down the number of beats per minute.
- Work out the average. This is what is called average heart rate per minute. It tells you how fast your heat is beating.
Measuring the pulse rate
EXPERIMENTATION
Biology as a science subject involves practical work. In every area of biology, experimentation is necessary. However, there are several procedures to be followed in conducting any scientific investigation. These procedures include the following:
Identification of a problem (problem statement)
In our day to day life we often come across questions or phenomena which require explanations. Such questions or phenomena are of interest to a biologist who will seek to provide answers to them.
The phenomena could be for example; it was observed that the harvest of tomatoes in Juma’s garden was low despite frequent irrigation, correct planting techniques, timely planting and adequate sunlight. So, what was the problem with Juma’s garden?
This is the problem to be investigated by the biologist in order to come up with an answer.
Hypothesis formulation
Hypothesis is a tentative explanation for the observation made. Using your example of low yield in the tomato garden, the possible hypothesis could be poor yield could have been caused by low soil fertility and therefore application of the fertilizer could increase harvest of the tomatoes in the garden. This hypothesis must therefore be tested by experimentation if it has to be a scientifically acceptable explanation.
Experimentation
An experiment is a series of investigation intended to discover relationship or certain facts that may lead to finding a problem. In the case of low harvest of tomatoes, you are first supposed to construct a plan of investigation as follows:
Select two plots, A and B, from the same garden and subject both of them to the same conditions as before. In plot B apply fertilizers while in plot A don’t put any fertilizers (plot A will be your control plot).
Observation and data recording
After setting up an experiment, a researcher must observe and record data. Observation is done by using sense organs such as ears, eyes, nose and skin. The researcher must record whatever he observes. The researcher obtained X kg in plot A and Y kg in plot B.
Interpretation of data
Once a researcher has collected data, he should try to explain the meaning of data in relation to the purpose of the experiment. In the tomato garden experiment, the harvest in plot A was little compared to the harvest in plot B.
In these plots, all the conditions were the same except that in plot A no fertilizers were applied while in plot B fertilizers were applied. Therefore, high harvest in plot B was a result of applying fertilizers. If this experimentation is correct, then the same results should be obtained if the experiment is repeated under the same conditions.
Conclusion
At the end of investigation, a researcher must draw conclusion. This conclusion is based on the collected data. The conclusion is either confirmation or rejection of the hypothesis under investigation.
In the tomato garden experiment, the results have shown that application of fertilizers has increased the harvest of tomatoes. Therefore, low harvest of tomatoes was caused by poor soil fertility.
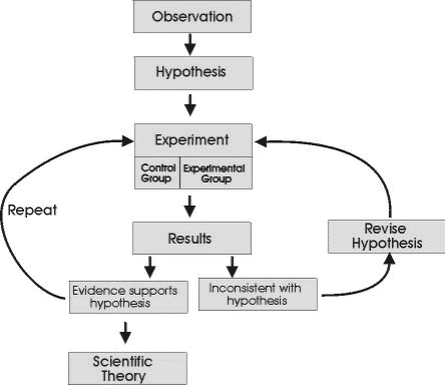
Summary
The following diagram summarizes the scientific process.
The scientific process
Activity 2
Aim: observing different conditions and substances using various sense organs: Materials: flowers of different colors, hot water, ice, a bottle of perfume, whistle, lemon, knife.
Procedure:
- Take the different flowers provided. Name the color of each flower.
- Open the bottle of perfume, try to smell it. What is the smell of the perfume?
- Use a knife to cut the onion. Where in your body do you feel sensation when cutting the onion?
- Take two beakers. One of the beakers put hot water and the other put ice block with a little amount of water. Dip a finger in a beaker containing hot water and do the same for a beaker containing ice block. What sensation did you feel in the two beakers?
- Take a whistle and try to blow it using your mouth. What is coming out of the blow?
For each of the stimulus experienced in procedures 1-5 name the sense organ involved in detection of each stimulus and present your results as shown in the table below. The first option has been done for you as an example.
| Procedure | Stimulus | Sense organ involved for detection |
| 1 | Colour | Eyes |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 |
Activity 3
Aim: measurement of length and masses Materials: meter rule, Tilapia fishes, board, weighing scale
Procedure:
- Take 5 Tilapia fishes and number them as 1 to 5.
- Take Tilapia fish number 1, place it on a board and measure its length.
- Take Tilapia fish number 1, put it on a weighing scale and record its mass.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for Tilapia fish number 2, 3, 4, and 5.
Present your results in a tabular form as shown
| Tilapia fish no | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 |
Activity 4
Questions
- Which Tilapia has the greatest length?
- Which Tilapia has a greatest mass?
- Is there any Tilapia fish which has a shorter length but has a greater mass than the longer one?
- Arrange the fishes in order of their increasing
One of the following can be used to make observation during scientific investigation
- Nose
- Blood vessels
- Teeth
- Lung
All of the following are used for various measurements except
- Beam balance
- Thermometer
- Ruler
- Hand lens
Which of the following is not true?
- Eye for sight
- Skin for touch
- Tongue for vision
- Nose for smell
Body temperature can be measured using
- Chemical balance
- Stop watch
- Measuring cylinder
- Thermometer
A third step in scientific investigation is
- Hypothesis
- Problem identification
- Experimentation
- Conclusion
Hypothesis means
- An idea
- A school of thought
- An intelligent guess
- An opinion
Which of the following will be a sequence to follow in a scientific procedure after ‘experimentation’?
- Problem identification
- Conclusion
- Observation and data recording
- Hypothesis formulation
An experiment is carried out to test
- Hypothesis
- Theory
- Law
- Conclusion
Name the instruments used to measure
- Mass
- Length
- Pulse rate
- Temperature
Name the five sense organs used to make observation during scientific investigation and state the senses perceived by each sense organ.
Outline the six steps involved when carrying out scientific investigation.
Define the following terms:
- Hypothesis
- Experimentation
Simple Biological Experiments
Carry out simple biological experiments
Activity 5
Carry out a simple biological experiment in relation to the above topics.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments
(
Atom
)




No comments :
Post a Comment